Food manufacturing is a broad industry that employs many managers and professionals. Top executives decide policy and organize production operations. The day-to-day operations of a manufacturing facility are managed by industrial production managers. Marketing, community relations, sales, marketing and public relations managers direct the sales and promotional programs.
The food manufacturing industry has many jobs
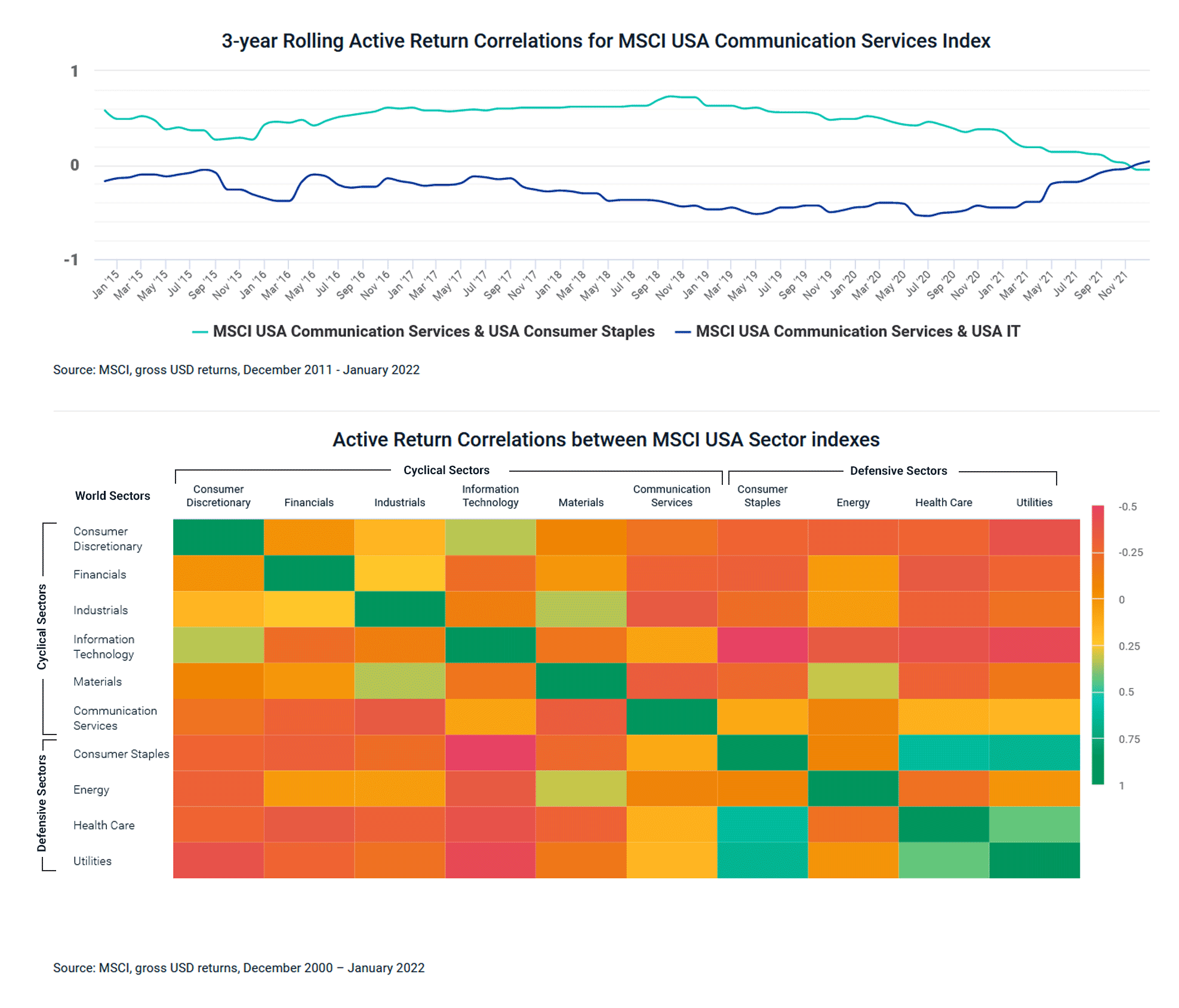
New York State is home to many food production jobs. The top three occupations include bakers, food batchmakers, and packaging and filling machine operators. These occupations comprise just over half of state's food production employment. Food manufacturing employment increased across the state in seven out 10 labor markets.
The improving job market is also responsible for the increase in food production jobs. In February, the unemployment rate was 3.8%, the lowest level in more than a decade. Nondurable goods industries saw the largest increase in employment in food manufacturing, with 16,000 additional workers.
Average wages in the industry
Average wages in food manufacturing are between $26,000 and $52,000 per annual, with the highest earners earning $52,000 per calendar year. The range is higher for those with more years of experience, but the bottom 10 percent of earners earn less than $26,000 per year. Food Factory Workers can earn a lot, but the salary range is not as wide as those in other industries.
The average wage in this sector has increased in the past few years. The manufacturing industry plays a vital role in our economy. But it's not an industry that is isolated. It is important to understand how the other parts of the economy affect the lives of workers.
Localities with the greatest number of workers
Food manufacturing firms concentrated in three New York State labor-market regions in 2013, the Finger Lakes and the Southern Tier. Combined, these three regions employed almost half the food manufacturing workforce. These regions were home to the largest concentration of food production. They also had the highest average salaries in Western New York, Southern Tier, or Hudson Valley.
Food processing is an industry that requires skilled labor. Food processing companies are struggling to find skilled workers due to a lack of workers in certain areas. Not only is it hard to find people to work in distribution trucks and other lower-level positions, but it's also becoming increasingly difficult to fill more senior positions. Career site CareersInFood.com reports that food manufacturing job openings have increased by 12% in the last year. There has been a 37% increase in the 24 months.

Industry: Number of workers
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics the number of food industry workers increased by 7.200 in February. This is a more than 1% increase from January. This month marks the third consecutive month with job gains in this industry. However, it is still struggling to recover from several headwinds. The global recession, the COVID-19 epidemic, and a labor shortfall have all had an impact on the industry's job prospects. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the industry employed 40,700 people in February.
New York State's number of food processing firms grew by 8.8% between 2003-2013. Four of the 10 labor markets saw an increase in employment, with the greatest increases being in the Southern Tier or Hudson Valley.
FAQ
How can we improve manufacturing efficiency?
The first step is to determine the key factors that impact production time. We then need to figure out how to improve these variables. If you don’t know how to start, look at which factors have the greatest impact upon production time. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
What types of jobs can you find in logistics
Logistics can offer many different jobs. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transport drivers - These are people who drive trucks and trailers to transport goods or perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – They manage the inventory in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products.
-
Logistics coordinators – They plan and coordinate logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service agents - They answer phone calls and respond to emails.
-
Shipping clerks – They process shipping orders, and issue bills.
-
Order fillers are people who fill orders based only on what was ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
How can manufacturing overproduction be reduced?
It is essential to find better ways to manage inventory to reduce overproduction. This would reduce the time needed to manage inventory. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
A Kanban system is one way to achieve this. A Kanban board, a visual display to show the progress of work, is called a Kanban board. Kanban systems are where work items travel through a series of states until reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
As an example, if work is progressing from one stage of the process to another, then the current task is complete and can be transferred to the next. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This allows work to move forward and ensures that no work is missed. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This information allows managers to adjust their workflow based off real-time data.
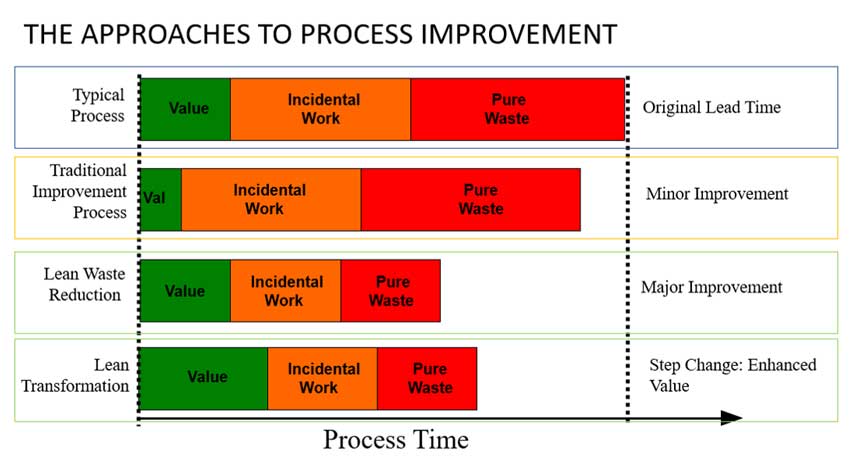
Lean manufacturing is another option to control inventory levels. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating waste from all stages of the production process. Anything that does nothing to add value to a product is waste. The following are examples of common waste types:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Packaging that is not necessary
-
Material surplus
Manufacturers can increase efficiency and decrease costs by implementing these ideas.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
What are the 4 types manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process by which raw materials are transformed into useful products through machines and processes. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use 5S for Increasing Productivity in Manufacturing
5S stands as "Sort", Set In Order", Standardize", Separate" and "Store". Toyota Motor Corporation created the 5S methodology in 1954. It helps companies achieve higher levels of efficiency by improving their work environment.
The idea behind standardizing production processes is to make them repeatable and measurable. It means tasks like cleaning, sorting or packing, labeling, and storing are done every day. Workers can be more productive by knowing what to expect.
Implementing 5S involves five steps: Sort, Set in Order, Standardize Separate, Store, and Each step has a different action and leads to higher efficiency. If you sort items, it makes them easier to find later. When items are ordered, they are put together. You then organize your inventory in groups. Finally, when you label your containers, you ensure everything is labeled correctly.
This process requires employees to think critically about how they do their job. Employees must understand why they do certain tasks and decide if there's another way to accomplish them without relying on the old ways of doing things. To be successful in the 5S system, employees will need to acquire new skills and techniques.
The 5S method increases efficiency and morale among employees. Once they start to notice improvements, they are motivated to keep working towards their goal of increasing efficiency.