
The Production Development Engineer is responsible for optimizing production processes in the manufacturing environment. It is responsible for creating a collaborative environment that will ensure the delivery of quality products on time. It is crucial that you are adaptable and innovative as well as a skilled communicator. You will also need to have a development-oriented mindset and strong analytical skills.
The Production Development Engineer is a member the Advanced Manufacturing Engineering Team and works in cross-functional groups. He/she will look for problems in current product and development processes and then use process tech to increase productivity and quality, decrease costs, and reduce cost. To solve technical problems, the Production Development Engineer may also collaborate with external vendors.
This position requires a bachelor of engineering degree. Candidates must have at minimum three years of manufacturing experience. Strong knowledge of Lean manufacturing is a plus. Understanding of technical communication programs and report writing is essential. You can make a valuable contribution to the Production Development Team if you are passionate about innovative solutions and cost-effectiveness.
The product engineers are those who create new products. Their duties include identifying consumer needs and preferences, analyzing data, and developing product prototypes. They also perform quality control procedures and provide specifications for production. They also examine and test the product for any defects or design tolerances. These tasks require strong mathematical and analytical abilities.
The Production Development Engineer who succeeds will be innovative and efficient. He or she must not only be creative in designing new products but also be able meet the budgetary expectations and satisfy stakeholder needs. This requires extensive industry experience in product design and an understanding of manufacturing processes.
Product engineers usually work in specific areas like electrical, software, and materials. Other areas of expertise may include optics, mechanics, and testing. The production engineer will be involved in every phase of the production process during the course of a project. Producing a new product requires that the production development engineer ensures that the equipment and methods used meet the quality, cost and time goals.
During the product's design phase, the Product Development Engineer will investigate and test the product to identify any potential problems or design tolerances. Next, the Product Development Engineer will design a new prototype using built-in control elements that help to save money during manufacturing.
Once the design has been finalized, the Product Development Engineer will coordinate production activities and other departments. Finally, he/she will create a quality assurance program to ensure the product meets specifications. This includes all safety and environmental issues. Finally, the engineer will deliver approved product plans to the production team.
The Production Development engineer must be proficient in 3D modeling and surface modeling software. It is an advantage if the candidate has experience in the assembly industry.
FAQ
What makes a production planner different from a project manger?
A production planner is more involved in the planning phase of the project than a project manger.
How important is automation in manufacturing?
Automation is essential for both manufacturers and service providers. It allows them provide faster and more efficient services. They can also reduce their costs by reducing human error and improving productivity.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. You don't have to know about manufacturing processes before learning about logistics. But, being familiar with manufacturing processes will give you a better understanding about how logistics works.
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling involves the assignment of dates and times to tasks in order to complete them within the timeframe.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the first book on lean manufacturing in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing can be described as just-in–time (JIT), total productive maintenance, zero defect (TPM), or even 5S. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
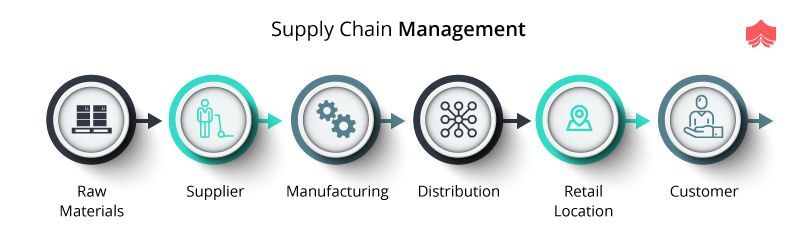
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow - Ensure work moves smoothly through the process without interruption.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
You can apply Lean Manufacturing to virtually any aspect of your organization. It is especially useful for the production aspect of an organization, as it ensures that every step in the value chain is efficient and effective.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement involves continuous improvement of processes.