
What is Manufacturing? Manufacturing is an added value process that creates goods. It involves the use of labor, machines, tools and chemicals to create goods and services. The secondary sector includes manufacturing. This process uses both manual and intelligent labor to create goods. Here are some benefits of manufacturing. Let's take a look at manufacturing and its benefits. You can then apply this knowledge to your own business.
Manufacturing is a subsector within the economy
The primary function of manufacturing is to create goods and services. It is also a subsector in the economy. It requires labor, equipment, and tools to complete production processes. These processes can involve chemical or biological processing. Manufacturing is, in essence, the heart of the secondary sector. Manufacturing is important to many different sectors of the economy, but it has its own unique advantages. These are just a few of the benefits.
A strong and vibrant manufacturing industry is key to the U.S.'s economy. While many economists view manufacturing as a consumer-oriented industry, others view it as a wealth-producing industry. Manufacturing jobs are essential to the economy as they create middle-class jobs and boost overall wealth. Manufacturing is a job-creating industry that spurs innovation and boosts the economy.
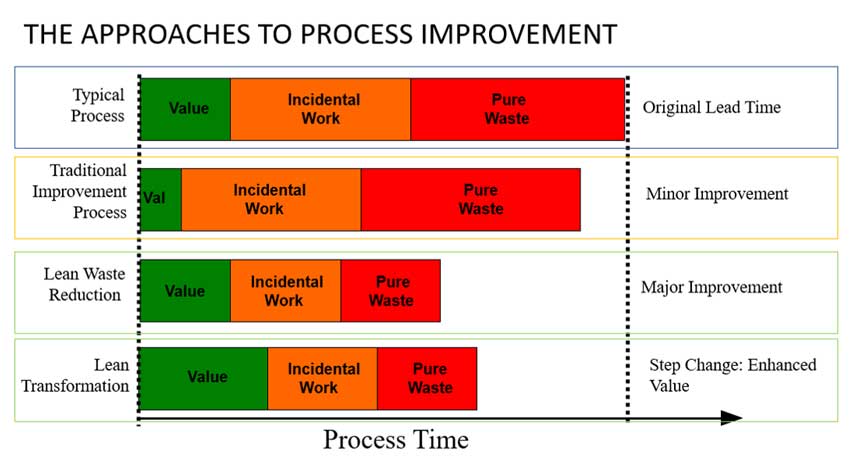
It adds value to your business.
Activities that affect the shape or quality of a product in the manufacturing industry are known as value-adding. Cleaning equipment, getting material and lining up equipment are all non-value-added tasks. They also include sorting items for pickup orders, printing paperwork, searching for locations, and searching for them. Automation can improve the manufacturing processes by automating other non-value-added functions. These are just a few examples of the activities that can easily be automated
Increasing productivity. Automation and computer technology can be used to increase productivity and lower costs. The United States government supports manufacturing. This involves large-scale production and physical transformation. Many industries have been highly successful through manufacturing, and many companies are successful due to their ability to produce goods on a large scale. Manufacturing is an important aspect of our economy and should be studied closely.
It employs manual labour
"Manual labour" is defined as physical work done by humans. It is distinct from work done by animals or machines. Manual labour refers to any physical labor performed with the hands or any other part. Manual labour has been the principal method of physical work for most people throughout human history. Here are some examples. 1. Agriculture: Most farmers use manual labour, which is often anchored to the crops.
There are many reasons that manual labour is often correlated with unskilled. Intelligence can be applied to almost any job, whether it's in artisanal craft production or logic in applied science. However, most workers do not have any formal training. Education has become an increasingly important part of modern life, but not everyone is able to have a broad range of experiences. As a result, some jobs require workers to perform certain tasks but not all.

It uses smart technology
Smart manufacturing is the integration of information technology in manufacturing processes, increasing adaptability, using web-connected machinery and optimizing performance. It involves a collaborative approach between employees and machines, using data analytics to improve production and profit margins. Smart factories feature highly automated systems and interoperable controls. They also have networked sensor networks. They can respond quickly to changes in demand and improve output and quality. Smart manufacturing isn't limited to one industry.
Artificial intelligence allows factories to detect problems and schedule maintenance before it becomes critical. These advanced technologies can monitor and respond to supply chain changes, reducing downtime costs. Smart factory technologies allow for automation of certain processes. This allows engineers to focus on more complex tasks. Smart factories have high upfront costs, so many small companies will not be able to invest in them. These technologies are important, but they are an integral part of manufacturing operations.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing has seen automation take center stage. Increased demand for efficient and faster delivery has resulted in a rise in e-commerce.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. In order to do this, they need to invest in technology. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Safety Boosts
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
It reduces downtime, and increases uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Eliminates human error
-
This helps to ensure compliance with regulations
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
A production planner makes sure all project elements are delivered on schedule, within budget, as well as within the agreed scope. A production planner ensures that the service and product meet the client's expectations.
How can efficiency in manufacturing be improved?
The first step is to identify the most important factors affecting production time. Next, we must find ways to improve those factors. If you don’t know how to start, look at which factors have the greatest impact upon production time. Once you've identified them, try to find solutions for each of those factors.
What skills are required to be a production manager?
You must be flexible and organized to become a productive production planner. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
How can I learn about manufacturing?
Practical experience is the best way of learning about manufacturing. You can read books, or watch instructional videos if you don't have the opportunity to do so.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics.
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was developed by International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL), and published as part of their "Seven Principles of Logistics Management Series" in 2004.
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsive - ensure all actions are legal and not harmful to others.
-
Reliable: Have faith in your ability or the ability to honor any promises made.
-
Use resources effectively and sparingly.
-
Realistic - Take into consideration all aspects of operations including cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and other factors.
-
Respectful - treat people fairly and equitably.
-
Responsive - Look for ways to save time and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-intime (JIT), which is a method to minimize costs and maximize efficiency in business process, is one way. It's the process of obtaining the right amount and timing of resources when you need them. This means that you only pay the amount you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He decided that workers would be more productive if they had enough time to complete their work before they started to work.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This way, you won't end up paying extra money for things that weren't really necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will enable you to keep track of how much material is left after you use it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: You stock materials in advance to make your projects easier. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is similar to cost-based but instead of looking at individual workers' salaries, you look at the total company price.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT: This is another variation of resource based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-intime (JIT), planning is a combination JIT management and supply chain management. It is the process of scheduling components' delivery as soon as they have been ordered. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.