
Dallas's manufacturing industry is vibrant, large, and growing. The city is known for its world-class reputation in manufacturing consumer goods, medical devices and computer systems. And it is a top destination for high-tech firms like Texas Instruments and Lockheed Martin, which have major plants in the Dallas area.
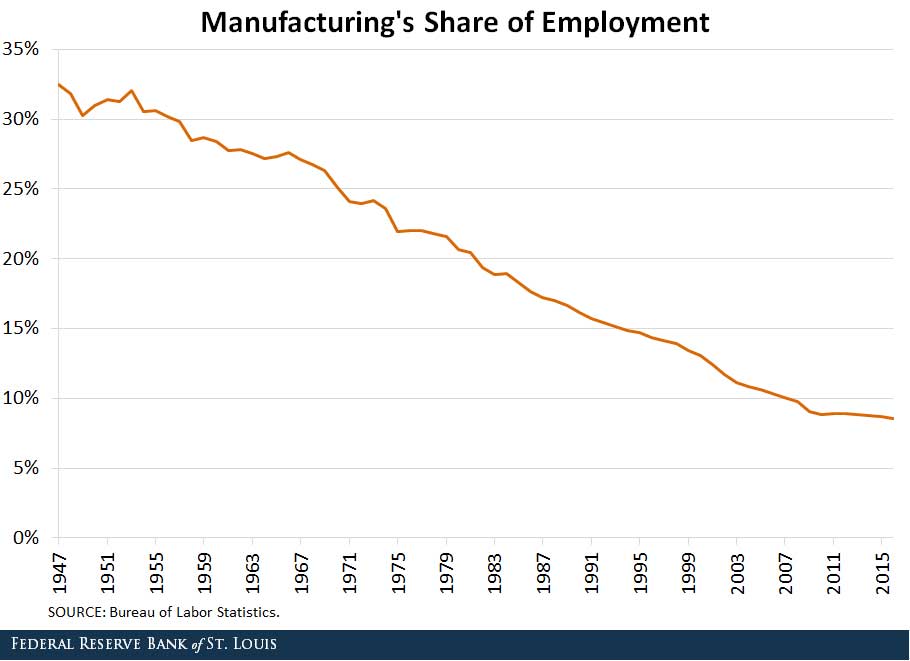
Dallas Fed, who conducts a monthly survey of the state's factories, estimates that the manufacturing sector grew by 3.5 per cent in 2016, which is slightly below the overall growth rate for the economy. Manufacturing is estimated to support about 2.2 millions jobs. This includes those in related industries such as distributors, service providers and transportation companies.
Computer and electronic product manufacture is an important subsector that accounts for about 28.7 billion Gross State Product in Texas in 2015 (the last available GSP data). The Brookings Institution considers computer and electronic products manufacturers to be advanced manufacturing industries because they have a high share of workers with higher levels of scientific knowledge than the national average.
Machine tool and machinery manufacturing is another substantial manufacturing subsector in Texas. It includes makers of agricultural, construction, mining and industrial machinery. TWC reports that this subsector accounts for about 88,000 manufacturing jobs and another 117,000 indirectly.
This highly-industrialized subsector supports an enormous number of jobs across other sectors. It contributes around $11.3 billion annually to the economy and pays an average salary of approximately $98,000. It employs an important number of engineers.
Metal fabricators produce everything from cutlery, to shipping containers. Houston's subsector employs 118,000 Texans.
TWC's estimates indicate that during the oil slump of 2015, this sector lost a few positions. However, in 2016, it recovered rapidly. The subsector is comprised of manufacturers of boilers, valves and heat-exchangers for the chemical and petrochemical industries along upper Gulf Coast.
Other important subsectors of this category are automotive parts, equipment and parts for aerospace, and railroad rolling stocks. Brookings states that these industries all have highly developed research and developments per worker.
No matter if you are an experienced manufacturing veteran or you have just started out, you need to know how you can increase your value with the right skill set. It is best to work with a company that offers contract manufacturing services. They can offer you specialized expertise and services such as 6S and Lean manufacturing. These services help your business to be more competitive and increase your bottom line.
FAQ
How important is automation in manufacturing?
Automating is not just important for manufacturers, but also for service providers. Automation allows them to deliver services quicker and more efficiently. In addition, it helps them reduce costs by reducing human errors and improving productivity.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
What are manufacturing and logistic?
Manufacturing refers the process of producing goods from raw materials through machines and processes. Logistics includes all aspects related to supply chain management, such as procurement, distribution planning, inventory control and transportation. Logistics and manufacturing are often referred to as one thing. It encompasses both the creation of products and their delivery to customers.
What skills should a production planner have?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
What are the main products of logistics?
Logistics refers to the movement of goods from one place to another.
These include all aspects related to transport such as packaging, loading and transporting, storing, transporting, unloading and warehousing inventory management, customer service. Distribution, returns, recycling are some of the options.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. They help companies manage their supply chain efficiency by providing information on demand forecasts, stock levels, production schedules, and availability of raw materials.
They can also track shipments in transit and monitor quality standards.
Do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes before learning about Logistics?
No. No. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
What is the role of a production manager?
A production planner ensures all aspects of the project are delivered on time, within budget, and within scope. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just In-Time Production Method
Just-intime (JIT), a method used to lower costs and improve efficiency in business processes, is called just-in-time. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He observed how workers were paid overtime if there were delays in their work. He decided that workers would be more productive if they had enough time to complete their work before they started to work.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are several types of JIT techniques:
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is very similar to cost-based, except that instead of looking at how much each individual worker costs, you look at the overall price of the company.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. It is used when production goals are met while inventory is kept to a minimum.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.