There are several benefits of earning a Master of Science in Supply Chain Management. First, you will be able to take advantage of the increasing demand for supply chain managers. In addition to the benefits, this degree is also highly sought-after for its career potential. Find out more about the various program options and requirements for this degree. You can also get an insider's view of the cost. Find out more.
Opportunities for career advancement
An MBA degree in Supply Chain Management could help you be a supply management expert, and even bridge to other job positions. Supply chain management jobs are vital today and can bridge into other roles. A master's degree is in Supply Chain Management will give you an edge and a lucrative career. This degree opens up many career possibilities in many industries. So it's important you understand how to maximize your degree.

Education requirements
Rutgers Business School provides an online master in science supply chain administration program for 30 credits. This prepares students in one of most rapidly-growing fields of business. Many of the most successful companies in the world view supply chain management as a core competency. Therefore, they actively recruit for graduates. This program covers supply chain management in all its aspects, from basic operations to complex logistics.
Programs available
There are many Master of Science supply chain management programs that you can choose from if you want to be a supply chain manager. These programs will prepare for a career as a supply chain manager and provide the expertise and skills necessary to succeed. The Master's degree will typically require 30 credits, but your individual program may require fewer. You have the option to choose from a program with accelerated courses, asynchronous courses or a weekend format if you are looking for flexibility in your work schedule. To find out more about the different programs available, contact the graduate schools directly and ask about start dates, how many credits you can transfer, and whether or not they accept financial aid.
Cost
The MSSCM Master of Science in Supply Chain Management is much more affordable than other graduate programs. The MSSCM program is much less expensive than other graduate programs. Graduates can also earn a world-class degree for half the cost. Saint Louis University alumni and friends offer generous scholarships that allow students to pay much less for their education than they might imagine.

Program length average
A typical Master of Science in Supply Chain Management (MSSCM) program is 30 credit hours. This curriculum is for professionals who work. Through case studies and simulations, the curriculum emphasizes hands-on learning. Students will be able to gain real-world knowledge and then apply it in their job. This program is for students who have a bachelor's in engineering, business, economics or another related field.
FAQ
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling is the process that assigns dates to tasks so they can get completed within a given timeframe.
What are the main products of logistics?
Logistics refers to all activities that involve moving goods from A to B.
They cover all aspects of transportation, such as packing, loading, transporting and unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the right product reaches the right place at the right time and under safe conditions. They assist companies with their supply chain efficiency through information on demand forecasts. Stock levels, production times, and availability.
They can also track shipments in transit and monitor quality standards.
What are manufacturing and logistics?
Manufacturing refers to the process of making goods using raw materials and machines. Logistics covers all aspects involved in managing supply chains, including procurement and production planning. Sometimes manufacturing and logistics are combined to refer to a wider term that includes both the process of creating products as well as their delivery to customers.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
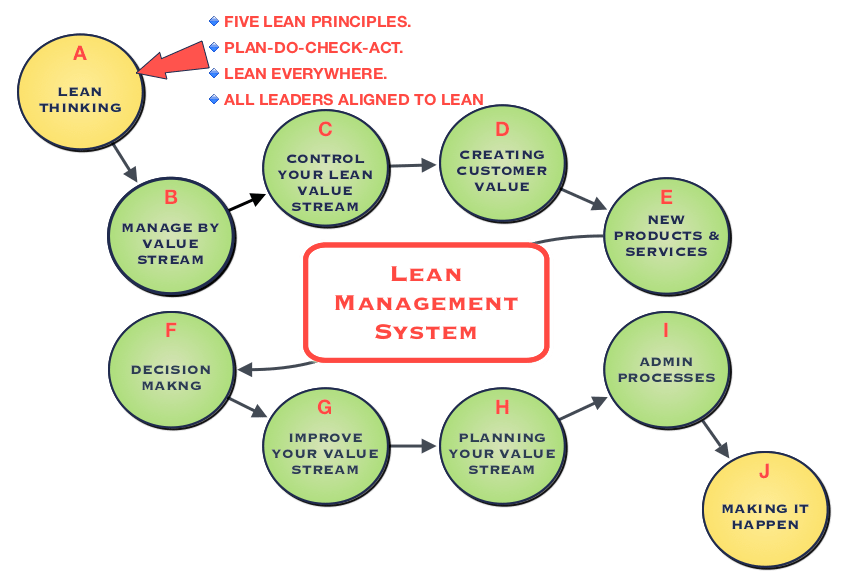
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was developed in Japan between 1970 and 1980 by Taiichi Ohno. TPS founder Kanji Tyoda gave him the Toyota Production System, or TPS award. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing can be used to manage all aspects of the value chain. Customers, suppliers, distributors, retailers and employees are all included. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow - Make sure work runs smoothly without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify – Make processes as repeatable and consistent as possible.
-
Build relationships - Develop and maintain personal relationships with both your internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has been gaining popularity over the last few years due to a renewed interest in the economy following the global financial crisis of 2008. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.