
Developing cutting edge manufacturing technologies is one of the primary aims of the National Network for Manufacturing Innovation. This interagency initiative was announced by President Obama in his FY 2013 budget proposal. It will bring together community colleges and universities engineering schools to help commercialize innovative manufacturing technology.
The United States' manufacturing sector plays a crucial role in the country's economy. American workers can find work in this area. In order to remain competitive, manufacturing companies are investing in technological innovations that help them stay productive while reducing labor costs. These innovations include automation as well as green energy sources. Companies are investing in ways to minimize machine downtime. These innovative products include autonomous mobile robots that reduce labor costs and increase productivity. Additionally, companies invest in technologies that reduce the waste of resources, such as smart sensor technology.
The "Maker's Economy," which is expected to transform the manufacturing process, will be revolutionizing how products are made. This is an economy where manufacturing users are actively involved in designing and building new products. These innovations are expected by the manufacturing sector, which is expected to benefit from them to increase productivity and operational efficiency as well as enhance decision-making. It is expected that it will also contribute to the nation's overall productivity. The United States is known for being a global leader when it comes to manufacturing.

The "Maker's Economy," relies on a variety technologies, including smart factories or artificial intelligence. These innovations improve manufacturing productivity by increasing worker efficiency and decreasing the amount of time it takes to produce a product. The Industrial Internet of Things is a network of sensors and data that guides tasks. It also allows continuous monitoring of industrial assets. Secure connectivity is crucial for IIoT. It is expected that it will improve warehousing efficiency as well as supply chain visibility.
The National Network for Manufacturing Innovation is composed of at least 15 manufacturing institutes. It is expected to accelerate the development and application of manufacturing technologies. The network will also include public/private partnership from both government entities and private businesses.
There are currently fourteen manufacturing innovation centers in the United States. Three more will be funded by Commerce Department in May 2013. Two Institutes will be funded by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. This will provide a total of up to $70 million per institute over five to seven years.
The Institutes for Manufacturing Innovation will each have a unique research concentration. They will act as innovation centers for the state and local economies. These Institutes will be able to assist manufacturers with their integration efforts. These institutes will offer manufacturers access to cutting-edge equipment and technologies as well as opportunities for workforce training. They will also help manufacturers solve cross-cutting challenges in advanced manufacturing.
The Network for Manufacturing Innovation serves a variety of purposes, including the acceleration of the commercialization of innovative manufacturing technology, bridging gaps between laboratory research and market applications, as well as strengthening state economies and local economies. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will run the institutes and the program will receive funding from the U.S. Commerce Department’s National Institute of Standards and Technology.
FAQ
What does it mean to warehouse?
A warehouse is a place where goods are stored until they are sold. It can be either an indoor or outdoor space. It could be one or both.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
What types of jobs can you find in logistics
There are many types of jobs in logistics. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers - They load and unload trucks and pallets.
-
Transport drivers - These are people who drive trucks and trailers to transport goods or perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - They oversee the inventory of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives: They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators: They plan and manage logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shippers clerks - They process shipping order and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - These people fill orders based on what has been ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There are many types of jobs in logistics such as transport supervisors and cargo specialists.
What skills are required to be a production manager?
A production planner must be organized, flexible, and able multitask to succeed. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
Are there ways to automate parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Automation has been around since ancient times. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Today, robots assist in the assembly of lines.
Robotics is used in many manufacturing processes today. These include:
-
Automated assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that produce products
There are many other examples of how manufacturing could benefit from automation. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management system that aims at increasing efficiency and reducing waste. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing can help companies improve their product quality and reduce costs. Additionally, it helps them achieve their goals more quickly and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing can be used to manage all aspects of the value chain. Customers, suppliers, distributors, retailers and employees are all included. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five basic principles of Lean Manufacturing are included in lean manufacturing
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. Some economists even believe that lean manufacturing can be a key factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
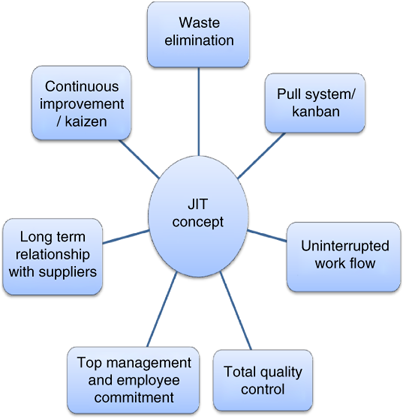
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This approach aims to reduce lead times, increase the availability of parts, and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.