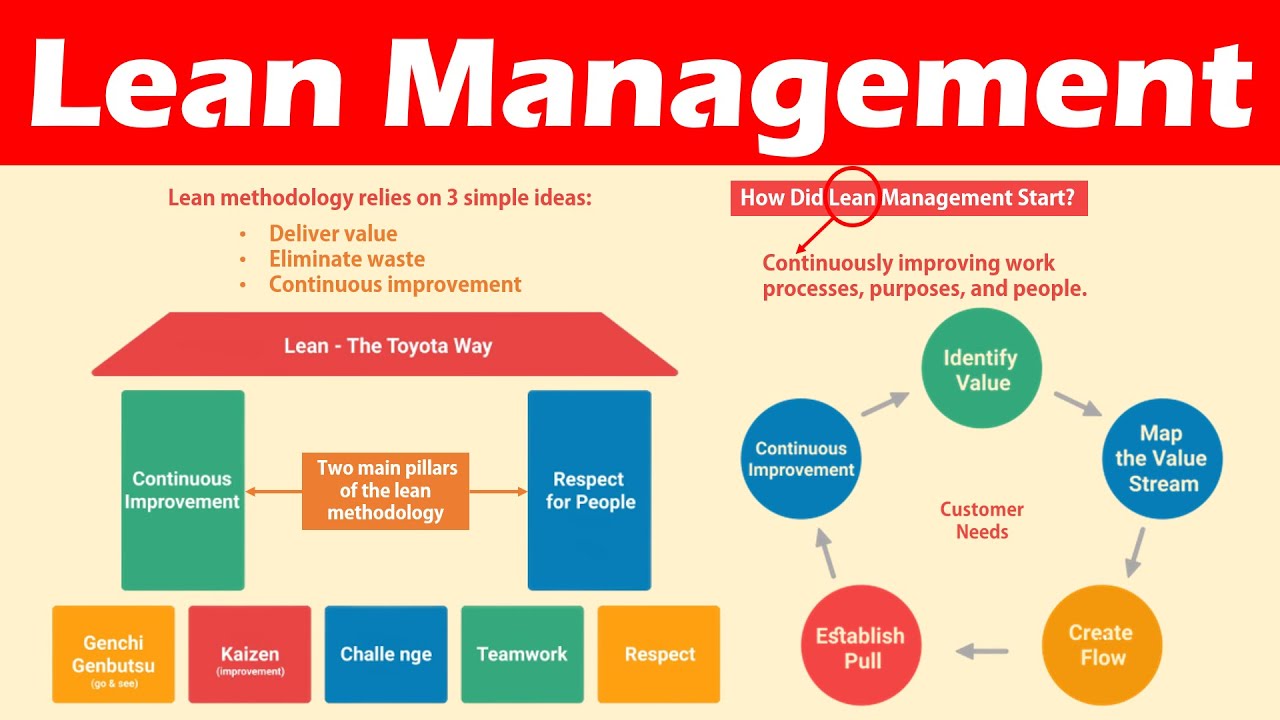
Although lean manufacturing offers many advantages, some companies have had difficulties implementing this strategy. Companies need to develop a comprehensive plan for overcoming these obstacles. Companies who have implemented Lean found three main problems that hamper the success rate of the initiative.
No matter how large a company is, lean manufacturing commitments are crucial to their success. Although there is no way to know how committed a company to lean manufacturing, it is essential that they educate their employees on the new corporate culture.
It is also important to ensure that resources are allocated correctly. Public organizations often find that they spend their budgets on unnecessary items. It has been reported that managers sometimes purchase equipment that they do not need to spend their budget. This can lead to operational bottlenecks and inefficient implementation of lean manufacturing.

Resistance to cultural change is one of the greatest challenges when implementing lean manufacturing. Many employees, especially those who have been with the company a long time, don't like change. Some employees will wait for the majority to speak up and convince them to move in a new direction. In order to break through this resistance, management must communicate the benefits of the program and explain why the change is necessary.
Another problem is the absence of a comprehensive strategic transformation plan. Companies often transform multiple business operations simultaneously, but it is crucial to have a long-term strategic plan. This strategy helps companies mentor future leaders, maintain competitiveness and improve operations. It helps to identify and fix operational bottlenecks, and to identify and address growth potential.
To overcome resistance, it is important to have training. A proper training program helps workers understand what their responsibilities are and what they can expect. They also acquire multi-skills which allow them to work more independently. Worker training also aids in problem solving, which allows them to maintain Lean through increased performance.
Management should engage with workers regularly to overcome resistance. Managers may put pressure on workers to follow instructions, but managers need to be open and honest with workers about why the change is needed. In some instances, managers were found to have given incorrect instructions to their workers, which resulted in ineffective implementation.
Managers need to be present at work, no matter how large or small the company. They can identify the areas where improvements can be made. They also need to develop structured training modules and acquaint staff with the introduction of new digital work tools. These tools, like 5S, help with visual management.
A clear vision is essential for lean manufacturing implementation. This vision should include the responsibilities for employees, a schedule and a method of measuring success.
FAQ
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. You don't have to know about manufacturing processes before learning about logistics. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
Why is logistics important for manufacturing?
Logistics is an integral part of every business. They are essential to any business's success.
Logistics are also important in reducing costs and improving efficiency.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics.
The acronym "7R's" of Logistics stands for seven principles that underpin logistics management. It was created by the International Association of Business Logisticians and published in 2004 under its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters form the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
It is reasonable to use resources efficiently and not waste them.
-
Realistic - Consider all aspects of operations, including environmental impact and cost effectiveness.
-
Respectful – Treat others fairly and equitably.
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable: Provide customers with value-added service
Are there ways to automate parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Automation has been around since ancient times. The Egyptians invent the wheel thousands of year ago. Nowadays, we use robots for assembly lines.
Actually, robotics can be used in manufacturing for many purposes. These include:
-
Assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots create products
Manufacturing can also be automated in many other ways. 3D printing makes it possible to produce custom products in a matter of days or weeks.
How can I find out more about manufacturing?
Hands-on experience is the best way to learn more about manufacturing. You can also read educational videos or take classes if this isn't possible.
What's the difference between Production Planning & Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), or production planning, is the process by which you determine what products are needed at any given time. This can be done by forecasting demand and identifying production capabilities.
Scheduling involves the assignment of dates and times to tasks in order to complete them within the timeframe.
What does it mean to be a manufacturer?
Manufacturing Industries are businesses that produce products for sale. These products are sold to consumers. These companies use various processes such as production, distribution, retailing, management, etc., to fulfill this purpose. They manufacture goods from raw materials using machines and other equipment. This covers all types of manufactured goods including clothing, food, building supplies and furniture, as well as electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles and pharmaceuticals.
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
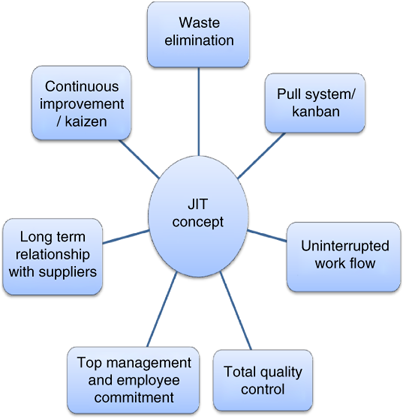
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means you only pay what you use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You'll be prepared to handle any potential problems if you know in advance. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven : This is a method where you make sure that enough money is set aside to pay the project's cost. When you know how much you need, you'll purchase the appropriate amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. You assign certain resources based off demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is very similar to cost-based, except that instead of looking at how much each individual worker costs, you look at the overall price of the company.
-
Material-based is an alternative to cost-based. Instead of looking at the total cost in the company, this method focuses on the average amount of raw materials that you consume.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based JIT : This is the newest type of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.