Industrial Engineering Managers play a vital role in the team, no matter if it's for a new project or routine work. They play a vital role in the management of staff members and improving output. This includes managing the factory floor's layout and design, and overseeing implementation of processes and procedures. Additionally, they offer technical knowledge and expertise that can be used to aid in the development of new products or processes.
The Industrial Engineering Managers are responsible to develop and maintain efficient manufacturing processes. This requires knowledge about the most recent trends in robotics and automation. They must also monitor and maintain industrial processes and ensure that they comply with safety and health standards. They are responsible for ensuring that raw materials and consumables are used properly. They also conduct studies to improve workflow and space usage. The manager is responsible for implementing all work projects. These include cycle time reductions, product cost reductions, and process improvements. They also manage preventative maintenance.
In collaboration with other teams, the manager develops new processes, streamlines operations, and improves efficiency. He or she also oversees the redesign and installation of equipment and facility renovations. The manager is responsible for communicating technical information to nontechnical stakeholders as part the project management process. Additionally, the manager ensures that resources are available to teams and makes site visits at suppliers' facilities. He/she advocates for team members, and ensures that quality compliance guidelines are followed.
Industrial Engineering Managers must be highly motivated and creative to solve problems. They must be able climb and walk for up to 12 hours per day, as well as be able handle extreme temperatures. In addition, they must be able to communicate effectively with all levels of employees.
A degree in engineering or another related field is necessary for industrial engineering managers. They must also possess at least five year's experience in the industry. Some employers prefer candidates with a postgraduate degree. Some employers prefer candidates with postgraduate education.
Industrial Engineering Managers oversee the design and development of new products and processes. They have strong skills in problem-solving, quality improvement, and other related areas. They thrive in a team environment. Managers are more successful when they are able to encourage employee growth.
Industrial engineers excel in streamlining operations. They are knowledgeable in manufacturing processes, and enjoy meeting deadlines. They have also worked in human resources, logistics and vendor/supplier relations. They are proficient in setting goals, administering procedures, and creating budgets. They can also create strategies to increase efficiency in engineering projects.

Industrial engineering managers may be responsible in designing and implementing new manufacturing techniques or operating equipment. They are responsible for developing plans to implement new equipment or operating methods according to established standards and guidelines. They must also oversee the process of implementing waste elimination plans. They are also responsible for analysing the productivity of the factory's workers.
Industrial Engineering Managers can help improve productivity and develop new products. They also have the expertise to manage human resources. They can also help develop and improve the efficiency of existing processes.
FAQ
What are the 7 Rs of logistics management?
The acronym 7R's for Logistics stands to represent the seven basic principles in logistics management. It was created by the International Association of Business Logisticians and published in 2004 under its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters form the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that actions are in compliance with legal requirements and do not cause harm to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
Use resources effectively and sparingly.
-
Realistic - Take into consideration all aspects of operations including cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and other factors.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
Resourceful - look for opportunities to save money and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable provides value-added products and services to customers
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
Can certain manufacturing steps be automated?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians created the wheel thousands years ago. Robots are now used to assist us in assembly lines.
In fact, there are several applications of robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Automated assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that make products
Automation can be applied to manufacturing in many other ways. 3D printing is a way to make custom products quickly and without waiting weeks or months for them to be manufactured.
What skills is required for a production planner?
You must be flexible and organized to become a productive production planner. Communication skills are essential to ensure that you can communicate effectively with clients, colleagues, and customers.
How can we improve manufacturing efficiency?
First, determine which factors have the greatest impact on production time. We must then find ways that we can improve these factors. If you aren't sure where to begin, think about the factors that have the greatest impact on production time. Once you have identified the factors, then try to find solutions.
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
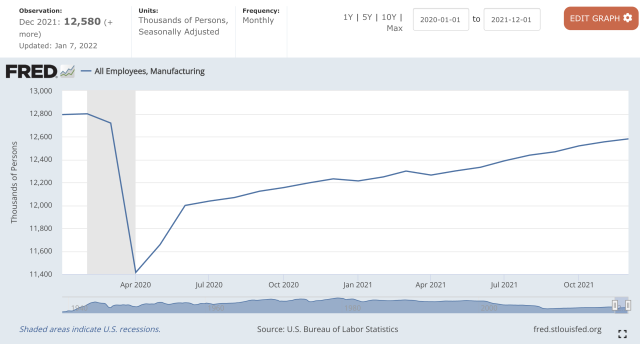
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
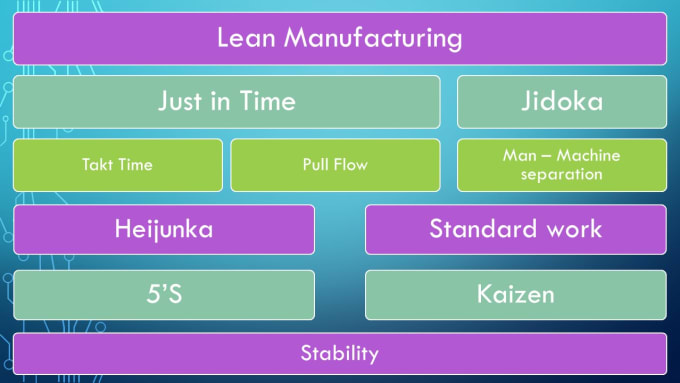
Lean manufacturing is often described as a set if principles that help improve the quality and speed of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. For example, Toyota's philosophy underpins its success in automobiles, electronics, appliances, healthcare, chemical engineering, aerospace, paper, food, etc.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow - Make sure work runs smoothly without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Building Relationships – Establish personal relationships with both external and internal stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.